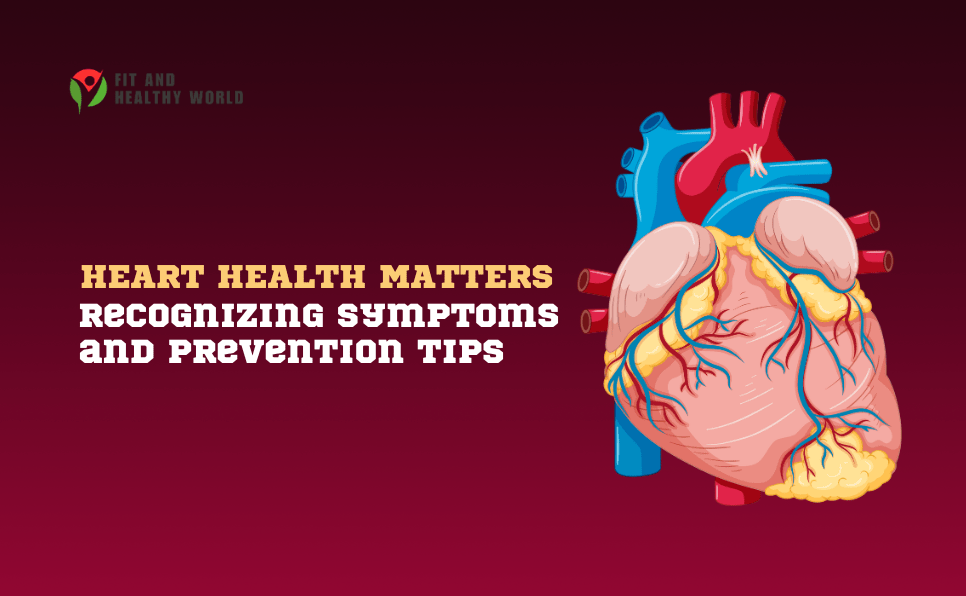
Heart disease continues to be a main global cause of death. By identifying the warning Symptoms of heart disease and knowing how to avoid it, you can take charge of your health. Heart health can be attained with early detection and possible actions. This book will help you keep your heart strong and healthy by explaining the signs, causes, and practical defensive activities.
Your heart is the engine of your body—nurture it well. Early detection and proactive care can turn potential threats into opportunities for a healthier tomorrow.
Recognizing the Cryptograms of Heart Disease
A diversity of heart-related illnesses is composed under the general phrase “heart disease.” Depending on the type of heart disease, these symptoms may vary, although they frequently have certain similarities.
What Signs Indicate Heart Disease?
At initially, heart disease symptoms may be mild, but they may eventually become more serious. Be mindful of:
• Chest Pain or Stiffness: Usually brought on by exercise or stress, this sensitivity is characterized by a heaviness, squeezing, or discomfort in the chest.
• Shortness of Breath: Living becomes difficult, particularly when training or when lying flat.
• Fatigue: Even after receiving enough sleep, feeling weak or bushed for no apparent reason.
• Swelling in the Extremities: Ankles, feet, or legs that swell due to fluid holding.
• Palpitations: Fast, erratic heartbeats that could look like flutters.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may come and go. Never ignore recurring symptoms, even if they seem minor.
Identifying Heart Disease Early Symptoms
Effective management of heart health depends on early identification. Although they should not be disregarded, early heart disease symptoms are frequently missed.
What Signs Indicate the Initiation of Heart Disease?
• Mild Chest Discomfort: This condition is sometimes confused with muscle strain or indigestion.
• Constant lightheadedness or dizziness: particularly after standing up or when exercising.
• Reduced Exercise Tolerance: Excessive fatigue following little effort.
| Symptom | Description | What to Watch For |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Discomfort | Pain, tightness, or pressure in the chest area. | Persistent discomfort that lasts more than a few minutes or recurs. |
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing, especially after minimal exertion or at rest. | Occurs even during light activity or while lying down. |
| Fatigue | Unusual or extreme tiredness without apparent cause. | Feeling constantly drained, even after adequate rest. |
How Do I Know If My Heart Is Harmful?
Some signs of an unhealthy heart include:
- Persistent smallness of breath.
- High blood pressure or cholesterol levels.
- Trouble sleeping or waking up sensation breathless.
A regular checkup with your doctor can deliver clarity about your heart’s condition and reveal hidden risk factors.
The 4 Signs of a Looming Heart Attack
A heart attack often comes with cautionary signs that, if recognized in time, can save your life. Look out for these symptoms:
- Intense Chest Pain or Pressure: May radiate to the arms, neck, or back.
- Severe Shortness of Breath: Often attended by a feeling of suffocation.
- Nausea or Sweating: Feeling clammy or wobbly, with potential vomiting.
- Sudden Fatigue or Weakness: A logic of overwhelming exhaustion.
These symptoms require direct medical attention. Call emergency services if you have a heart attack.
Specific Symptoms of Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease occurs when one or more valves in the heart do not function properly, troublesome blood flow.
- Unusual Heart Sounds (Heart Murmur): Often detected during a bodily exam.
- Fatigue or Fainting: Especially after physical action.
- Distension in the Abdomen or Legs: Due to fluid buildup.
Symptoms of Poor Movement and Heart Disease
Poor circulation often additions heart disease and can manifest in several ways:
- Stony Extremities: Constantly cold hands or feet due to limited blood flow.
- Blue-Colored Skin (Cyanosis): A sign of oxygen shortage in the blood.
- Pain or Constricting in the Legs: Often felt during walking or bodily motion.
Refining circulation through diet, exercise, and tablets can mitigate these symptoms.
How to Prevent Heart Disease?
Heart disease prevention starts with adopting a healthier routine. Lesser, consistent changes can yield significant grades.
Lifestyle Changes for a Healthy Heart
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Contain fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid trans fats and moderate sugar.
- Exercise Frequently: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and raises the risk of heart illness.
Treatment Risk Factors
- Control Blood Pressure: High blood pressure strains the heart. Monitor it frequently and make adjustments as wanted.
- Reduce Stress: Practice moderation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight growths your heart’s workload, important to higher risks.
Steps for Heart Disease Prevention
Steadiness is the substance of prevention. Follow these practical steps to maintain heart health:
- Start Minor: Begin with controllable goals, such as taking a 20-minute walk daily.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports universal health and circulation.
- Maximum Alcohol Feeding: Disproportionate drinking can increase blood pressure and cholesterol.
Your heart’s health is in your hands. Small, consistent changes in your lifestyle—like eating better, moving more, and managing stress—can lead to big results. A strong heart isn’t just a goal; it’s a commitment to living your best life every single day.
The Role of Regular Exercise
Physical action is a cornerstone of heart health. Both aerobic and strength-bodybuilding exercises offer unique benefits.
Aerobic Exercises
- Rambling, cycling, or swimming improves cardiovascular wellbeing and endurance.
- Aim for reasonable activity that increases your heart rate but is bearable.
Strength Training
- Builds muscle, boosts metabolism, and provisions overall heart function.
- Integrate light weights or resistance groups into your routine.
Living with Heart Disease
Many people with heart disease live long, fulfilling lives by accepting healthy habits and succeeding medical advice.
Can Someone with heart disease lead a normal life?
Indeed. People can preserve their quality of life by managing their health and changing their lifestyle. Among the most important advice is to eat a heart-healthy diet.
• Taking part in mild to moderate exercise.
• Stress management and putting mental health first.
The Expressive Impact of Heart Disease
Heart disease doesn’t just mark the body; it takes a toll on mental well-being as well.
- Coping with Anxiety: Practice mindfulness or seek psychotherapy to manage stress.
- Building Support Networks: Border yourself with friends, family, or support groups for inspiration.
Conclusion
A healthy life depends on knowing how to prevent heart disease and comprehending its signs. You may safeguard your heart health and general well-being by identifying early warning signals, leading a balanced lifestyle, and getting medical help when necessary. Keep in mind that even little actions can result in big gains. Prioritize heart health right now.
FAQs
What signs and symptoms indicate heart valve disease?
Corporate symptoms include exhaustion, limb edema, and irregular heartbeats.
What can I do to keep my heart healthy?
Maintain a healthy diet, do regular exercise, and abstain from smoking. For extra advantages, absorb to manage stress and obtain adequate sleep.
With heart illness, is it possible to lead a regular life?
Yes, many people enjoy happy, expressive lives with the correct treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
How is heart health improved by regular exercise?
Exercise increases circulation, strengthens the heart, and reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases.
Related to aerobic exercise, what are the compensations of strength training?
While strong point training helps to develop muscle and assist metabolism, cardio growths heart endurance. The best combo is both.
To preserve heart health, how much exercise is recommended for adults?
Weekly goals should include 150 minutes of reasonable aerobic exercise and two days of weight exercise.